Adsorption study comparing RSA™ to conventional glass autosampler vials.
Various test solutes were investigated in this study in order to determine the role that compound specific functional groups play in analyte loss to a vial. Percent loss increased in order of increasing number of amine froups and was greatest with permanently cationic species (thiamine and cetylpyridinium chloride).
Furthermore, percent loss was significantly lower using RSA™ glass vials, which show how the surface chemistry has real end user advantages for the analytical laboratory. This is due to the fact that RSA glass vials do not have the many surface hydroxyl groups (aKa silanols) that are found in both standard glass vials and market leading certified glass vials. 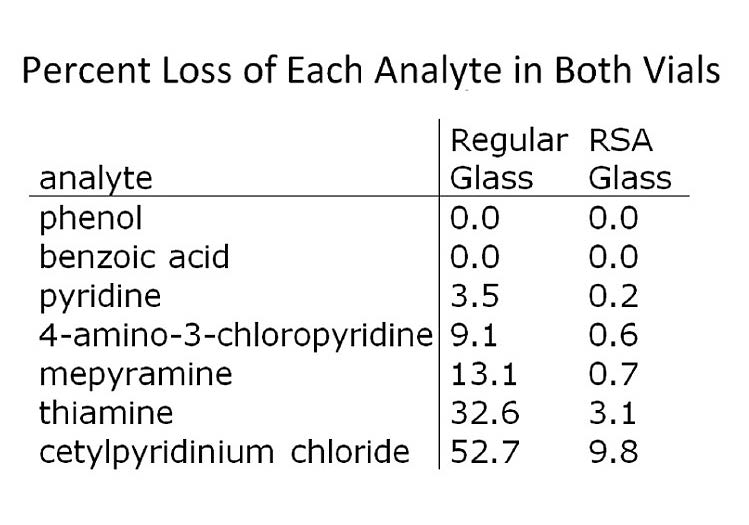
Method Conditions
Tested Items : RSA™, Glass Vials and AQR™ Screw Caps v. Market Leading Vials.
Specifications: Reduced Surface Activity Glass, Clear, 2ml, Write-On, Screw Top Vials and AQR Caps
Catalog No.: 9509S-1WCP-RS
Columns:
–Diamond Hydride™, 4μm,100Å
–Bidentate C18™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog Nos.:
—70000-10P
—40018-10P
Mobile Phase: Various Isocratic settings were used
Flow rate: 1.0mL / minute
Sample Preparation: 5.0ppm reference standards in DI water diluent. Portions of the same samples were transferred to the two vial types and injected into an HPLC initially and again after four hours. Peak areas were recorded and compared to initial injections to calculate percent recovery.
Attachment
Basic compound functional group dependent adsorption study in autosampler vials pdf Download File


