LCMS Method for Allantoin, 6-Aminouracil, and Uric Acid (UA)
The presented method for analysis of UA and its highly polar metabolites is simple and does not require Mobile Phase additives or pre-column derivatization. The Peaks are symmetrical, and the MS signal is not diminished, as is the case when Ammonium Formate or Acetate is used as a Mobile Phase additive.
The analyzed metabolites are signature end products for UA degradation in the presence of oxidants and can therefore be used as biomarkers for different disease states. Cogent columns can have very fast equilibration between gradient runs and can be successfully used in studies of pathways in human pathology.
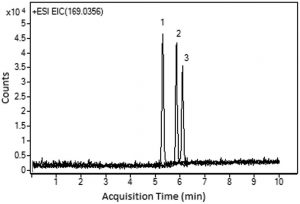
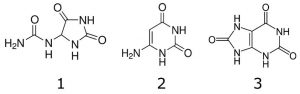
Peaks:
1. Allantoin 159.0513 m/z [M+H]+
2. 6-aminouracil 128.0455 m/z [M+H]+
3. Uric acid 169.0356 m/z [M+H]+
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Diol™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 40060-15P-3
Dimensions: 3.0 x 150mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 95 |
| 6 | 30 |
| 7 | 30 |
| 8 | 95 |
Flow rate: 0.4 mL/minute
Detection: ESI – POS – Agilent 6210 MSD TOF Mass Spectrometer
Injection vol.: 1μL
Sample Preparation: Standards of Uric Acid and its main metabolites were prepared in DI Water at concentrations of 20 microg /mL each. The sample for injection (a mixture of the three compounds) was diluted by a factor of 3.
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: Humans lack the enzyme (Uricase) which converts UA to Allantoin. However, the compound still can be detected in human Urine samples. UA can react with an oxidant in a step reaction and the end product is Allantoin. When UA is degraded it can’t be renewed. The presence of Allantoin in Urine is an indicator of a disease state (oxidative stress, renal failure, diabetes, etc.). The Allantoin/UA ratio is also elevated in Down syndrome and chronic lung disease. 6-Aminouracil is a direct product of reaction of UA with Nitric Oxide, which has a role in Cardiovascular disease.
Attachment
No 300 Uric Acid and Metabolites pdf 0.2 Mb Download File


