Separation from Matrix Peaks
Click HERE for Column Ordering Information.
Beta-carotene may be taken as a dietary supplement in capsule form. In this case, a wide variety of Matrix Peaks were observed in the chromatographic data. It is possible that some of these peaks are various isomers of all-trans ß-carotene or other similar carotenes. In any case, resolution was obtained from the other Matrix Peaks, which allows for accurate quantitation of ß-carotene in the capsule.
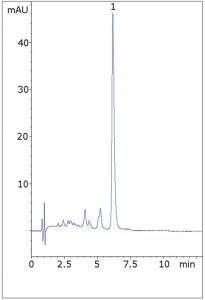
Peak:
ß-Carotene
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Phenyl Hydride™, 4µm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 69020-7.5P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75 mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 70 |
| 1 | 70 |
| 6 | 90 |
| 9 | 60 |
| 10 | 70 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Injection vol.: 10µL
Flow rate: 1.0 mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 452 nm
Sample Preparation: A Beta-carotene capsule was opened and the contents were transferred to a 25mL volumetric flask containing a portion of Methanol. The solution was sonicated 15 minutes and diluted to mark with Methanol. After mixing, a portion was filtered with a 0.45µm Nylon Syringe Filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp.).
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: Beta-carotene is found in many fruits and vegetables. It is responsible for the orange color in carrots, pumpkins, sweet potatoes, and others. In terms of nutrition, Beta-carotene is a metabolic precursor to Vitamin A.
Attachment
No 269 B-Carotene Capsule pdf 0.3 Mb Download File


