Potential Clinical Screening Method for Galactosemia
This Method is useful as a quantitative screening or routine clinical test to detect infants suspected of having a defect of Galactose Metabolism. It can also be used to monitor blood levels of Galactose-1-Phosphate in children with Galactosemia who are on a lactose-free diet.
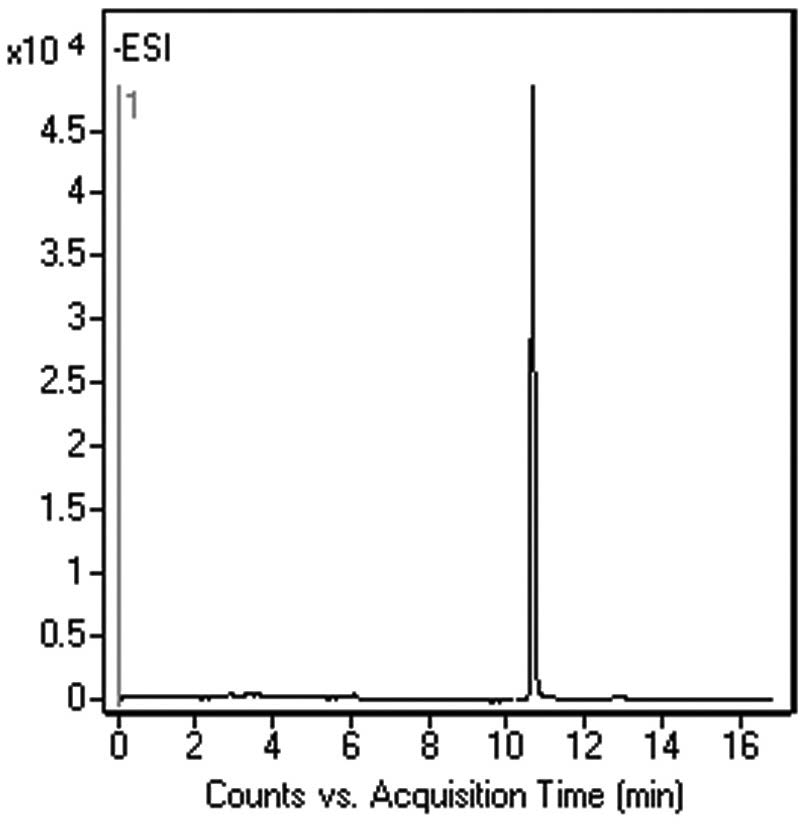
Peak:
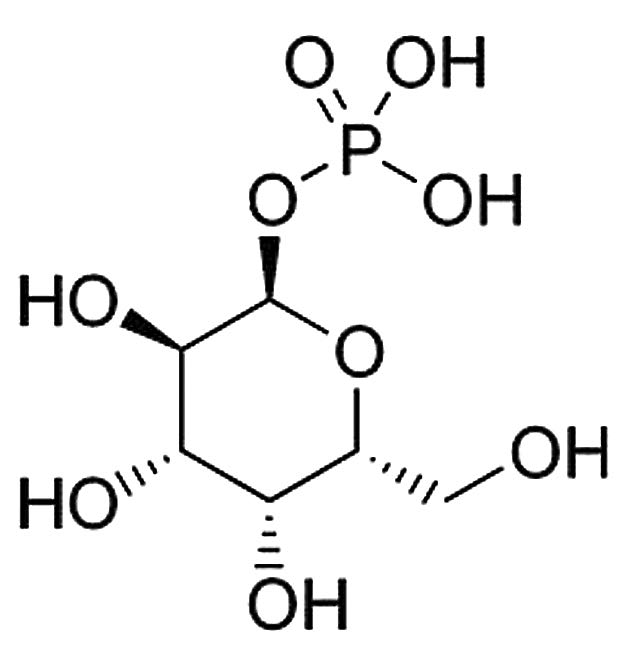
Galactose-1-phosphate, 259.0224 m/z (M-H)–
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-15P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 150mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water with 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: 90:10 Acetonitrile / DI Water with 16.5mM Ammonium Acetate (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 95 |
| 1 | 95 |
| 3 | 85 |
| 6 | 85 |
| 7 | 75 |
| 10 | 50 |
| 12 | 50 |
| 13 | 30 |
| 15 | 30 |
| 15.00 | 95 |
Post Time: 5 minutes
Injection vol.: 1μL
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Detection: ESI – NEG – Agilent 6210 MSD TOF Mass Spectrometer
Sample Preparation:
—Stock Standard: 1mg / mL Galactose-1-phosphate in DI Water, stored at -20°C.
—Working Solution: Stock was diluted 1:100 with 50:50 Acetonitrile / DI Water Solution.
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: The biochemical mechanism of (Gal 1-P) toxicity is still unknown. Recent experiments strongly suggest that Galactose-1-phosphate is also a substrate for Inositol Monophosphatase (IMPase). The brain is critically dependent on IMPase for the supply of free Inositol in order to sustain signaling. There is evidence which strongly supports the possibility that being a substrate, Gal 1-P could modulate IMPase function in vivo. This modulation has a role in a bipolar disorder.
Attachment
No 191 Galactose-1-Phosphate Analyzed with LCMS pdf 0.3 Mb Download File