Forced Degradation Method
Digoxin had several Sugar Residues that can be hydrolyzed in acidic conditions. In this Forced Degradation Method, six degradants are observed. Some of these Peaks are likely the various hydrolyzed forms, including the Aglycone Digoxigenin.
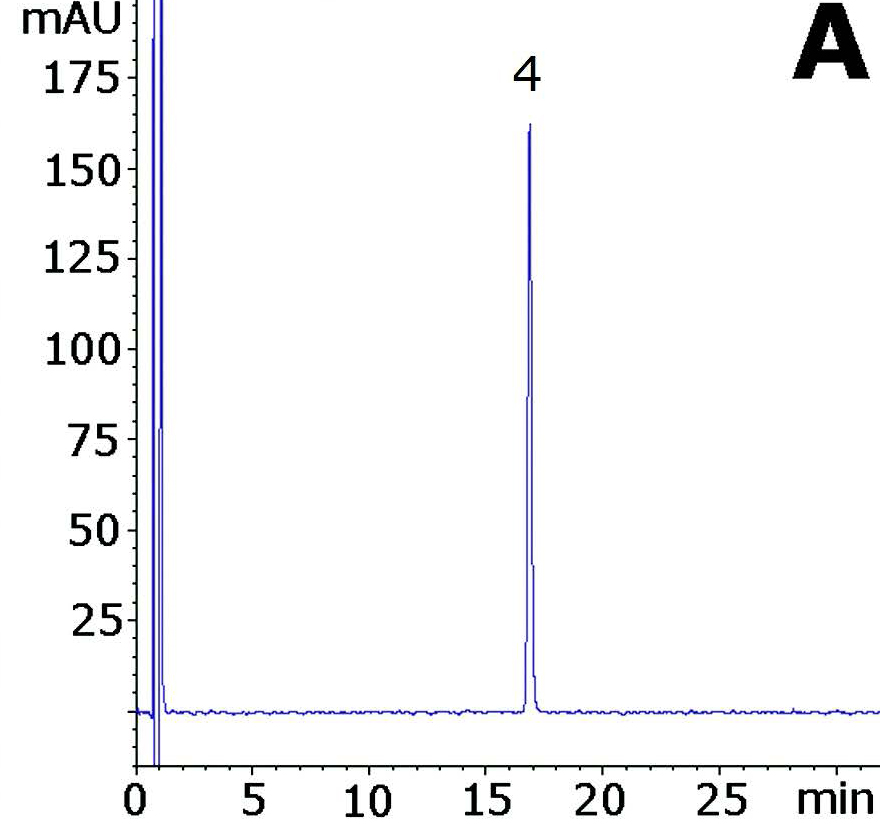
The Method is capable of Separating a wide variety of Degradants. Figure A shows the Chromatogram of the non-degraded sample while Figure B shows 5 consecutive runs of the acid degraded extract.
Peaks:
1–3. Degradants
4. Digoxin
5–7. Degradants
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Bidentate C18™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 40018-75P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 15 |
| 2 | 15 |
| 26 | 37 |
| 28 | 80 |
| 29 | 15 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Injection vol.: 10μL
Flow rate: 1.0mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 218nm
Sample Preparation:
—Figure A: Non-Degraded – 0.1mg / mL Digoxin in Methanol Diluent.
––Figure B: Acid Degradation – 0.1mg / mL Digoxin in 50:50 Methanol / 1N HCL Diluent. Sample was heated at 85°C for 10 minutes.
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside used to treat a number of heart conditions. It is a natural product obtained from the Foxglove Plant (Digitalis Purpurea). Accurate Quantitation of Digoxin is crucial since it is very toxic at higher levels.
Attachment
No 177 Digoxin Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.8 Mb Download File