Analysis of Composition using LCMS
Milk components are polar compounds that are not well retained or resolved by traditional Reversed Phase Chromatography. In addition, many of the compounds do not contain strong chromophores, resulting in low specificity and sensitivity in UV detection.
The analysis using the Cogent Diamond Hydride Column and MS detection provides separation and detection of all the compounds of interest. In this AppNote, The Diamond Hydride Column is able to analyze polar compounds in biological matrices.
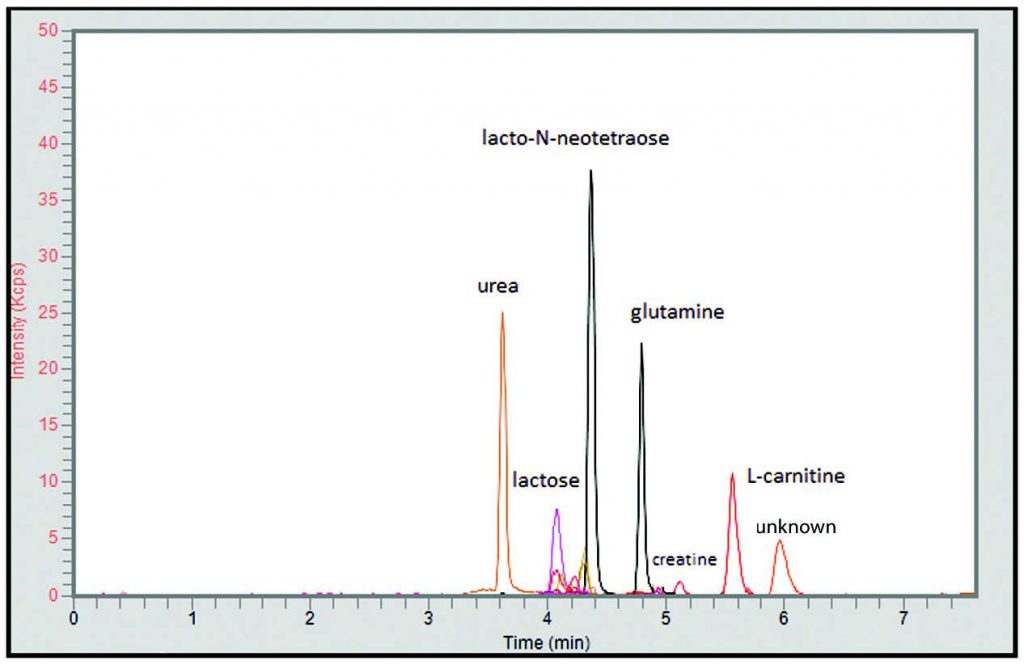
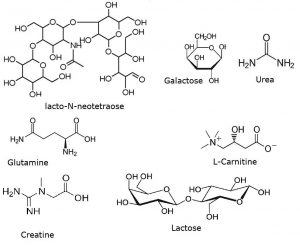
Peaks:
1. Urea 61.0396 m/z [M+H]+
2. Lactose 343.1235 m/z [M+H]+
3. Galactose 181.0707 m/z [M+H]+
4. Lacto-N-Neotetraose 708.2557 m/z [M+H]+
5. Glutamine 147.0764 m/z [M+H]+
6. Creatine 132.0768 m/z [M+H]+
7. L-Carnitine 162.1125 m/z [M+H]+
8. Unknown 105.1148 m/z [M+H]+
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-15P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 150mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 90 |
| 1 | 90 |
| 7 | 20 |
| 11 | 20 |
| 12 | 90 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Flow rate: 0.4 mL/minute
Detection: ESI – POS – PerkinElmer, Flexar SQ 300 Mass Spectrometer
Injection vol.: 1μL
Sample Preparation: Milk extract reconstituted in 65 micoL of 80% Acetonitrile / 20% DI Water
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: Milk was highly susceptible to microbial growth contamination prior to the advent of pasteurization. Named after the French chemist Louis Pasteur who invented it, pasteurization is a technique that extends the shelf life of milk by killing harmful microbes. In addition to his work in the field of microbiology, Pasteur also made significant contributions to our current understanding of chirality through the isolation of enantiomers of tartaric acid crystals.
Attachment
No 299 Milk Extracts pdf 0.4 Mb Download File


