High Efficiency Using a near-UHPLC Column for Oleuropein
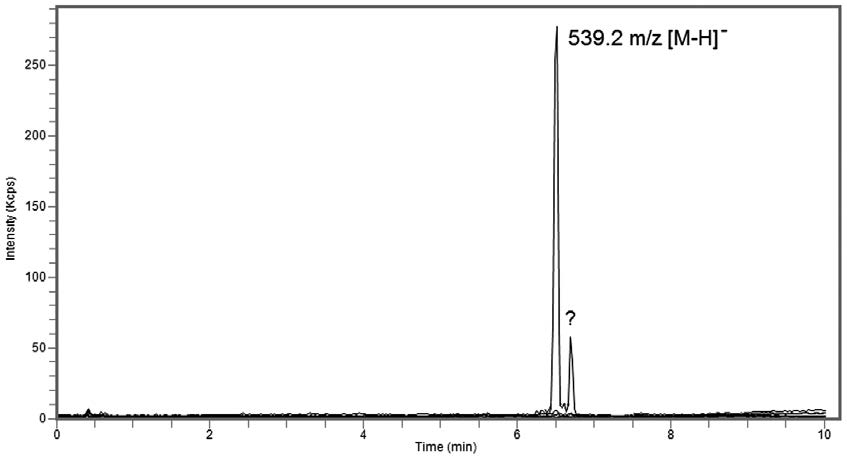
In this Application Note, the Analyte Peak is symmetrical and well Retained while the results were very reproducible (%RSD = 0.06 for Retention Times). This Method can be used to analyze and evaluate the extraction of Olive Leaves.
According to the literature, Olive Leave Extracts should contain the following compounds: Oleuropein, Hydroxytyrosol, Verbascoside, Apigenin, Luteolin-7-O-Glucoside, and Tyrosol [1].
Peak:
Oleuropein 539.2 m/z [M-H]–
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Bidentate C18 2.o, 2.2μm, 120Å
Catalog No.: 40218-05P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 50mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water with 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: Acetonitrile with 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 5 |
| 3 | 15 |
| 4 | 15 |
| 6 | 30 |
| 7 | 30 |
| 11 | 95 |
| 14 | 95 |
| 15 | 5 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Injection vol.: 1μL
Flow rate: 0.3mL / minutes
Detection: ESI – NEG – PerkinElmer Flexar SQ 300 Mass Spectrometer
Sample Preparation: Commercial Olive Leaves Extract was dissolved in DI Water at a concentration 10ppm.
t0: 0.6 minutes
Note: Olive Leaves are food byproducts (after pruning of Olive Trees) which are full of bioactive compounds. These compounds are potent polyphenols, which show antibacterial, antiviral, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities. Different extraction procedures are used for selective extraction of polyphenols from olive leaves. An analytical method to monitor and evaluate the resulting extract is needed.
[1] J.E. Hayes, P. Allen, N. Brunton, M.N. O’Grady, and J.P. Kerry, Food Chemistry, 126, (2011) 948–955.
Attachment
No 284 Oleuropein in Olive Leaves Extract Analyzed with LCMS pdf 0.2 Mb Download File