Methylenedioxymethamphetamine Analyzed with MS
Click HERE for Column Ordering Information.
Under the described conditions, MDMA was retained and eluted as a Symmetrical Peak. The Sensitivity of the Method is very good and comparable to that reported with GCMS Detection [1]. Matrix effects were of minor extent and reproducible and hence should not compromise Quantification. The Method can be used for Forensic Research and Clinical Analysis.
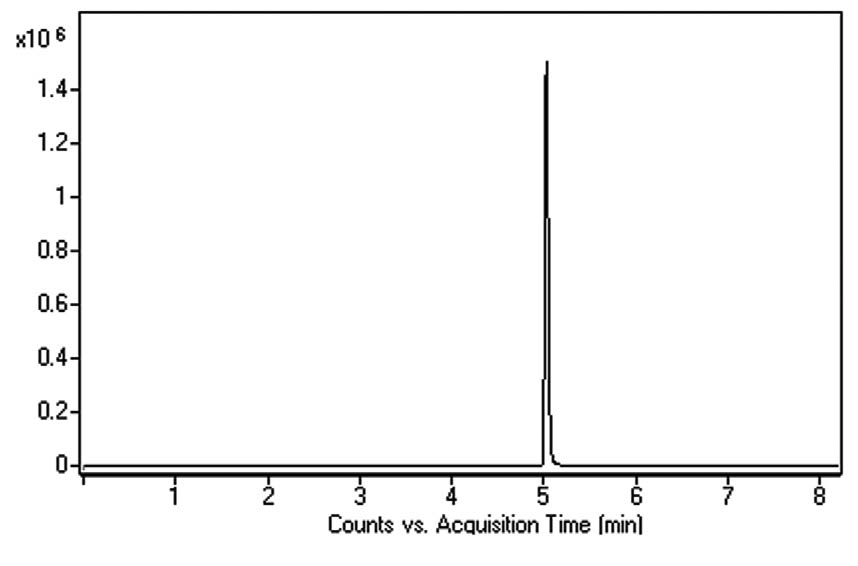
Peak:
(±)-3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine, m/z 194.1176 [M+H]+
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Phenyl Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 69020-05P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 50mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Formic Acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 10 |
| 1 | 10 |
| 6 | 90 |
| 7 | 10 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Injection vol.: 1μL
Sample Preparation: 50 μl of Acetonitrile was mixed with 50μl of plasma for protein precipitation. The samples were centrifuged (16000×g for 15 minutes), and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.45μm Nylon Syringe Filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp.) and transferred to autosampler vials for injection.
Detection: ESI – POS – Agilent 6210 MSD TOF Mass Spectrometer
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: The Amphetamine derivative 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), known also as Molly or Ecstasy, is often used or abused as a recreational drug. Because of a reported high inter-individual difference of its toxicity, sensitive analytical methods are needed. A urine test is a standard method to investigate drug abuse but the method has a very low diagnostic sensitivity and makes testing in plasma much more suitable.
Reference:
[1]. R. Kikura, Y. Nakahara, T. Mieczkowski, F. Tagliaro, Forensic Sci. Int. 84 (1997) 165–177.
Attachment
No 263 Analysis of MDMA in Plasma Samples with LCMS pdf 0.2 Mb Download File


