Everyday Reliable & Precise Method
This Method offers great Resolution of a mixture of four Sulfa drugs. These Antibiotics are commonly used in both veterinary medicine and also employed to fight disease in honey bees. The importance of quantification is vital, as residues are often found in honey samples and are of concern to customers due to allergic reactions.
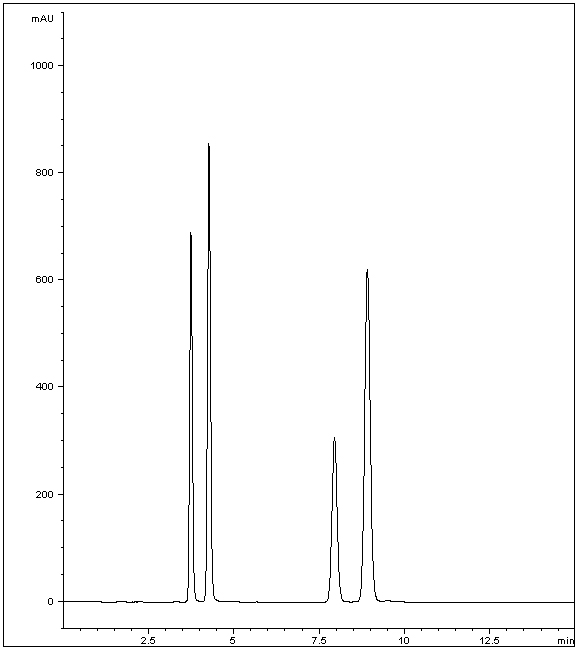
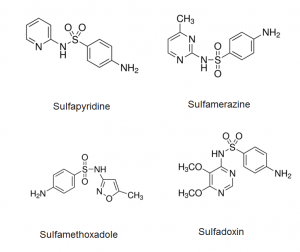
Peak:
1. Sulfapyridine
2. Sulfamerazine
3. Sulfamethoxazole
4. Sulfadoxin
Method Conditions:
Column: Cogent RP Phenyl Hexyl™, 5μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 68539-15P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 150mm
Mobile Phase: 75:25 DI Water with 0.1% Formic Acid / Acetonitrile
Injection vol.: 5μL
Flow rate: 1.0mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 270nm
Sample Preparation: 0.25mg / mL of each analyte in 50:50 Acetonitrile / DI Water
Note: Introduced in the 1930’s, Sulfonamide drugs paved the drug pathway as an antibiotic revolution in medicine. They were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically. Sulfonamides inhibit Dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS), an enzyme that is an essential nutrient and is critical for the synthesis of folate. Where mammals acquire folate from their diet, bacteria must synthesize this vitamin. Folate synthesis requires a chemical reaction between 2 molecules, DHPP and PABA, that is catalyzed by DHPS. Sulfonamides inhibit DHPS by binding to the active site. Once bacteria developed resistance, they were replaced by penicillin. Researchers found the bacteria resistant to sulfa drugs often have mutations in the DHPS enzyme.
Attachment
Sulfonamide Antibiotics Analyzed with HPLC pdf Download File


