Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Analyzed with HPLC - AppNote
April 22, 2021
/
/
/
/
/
Simple and Precise Retention of a Polar Antibiotic
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride requires the addition of buffers as well as ion pair reagents to aid in retention on regular Reversed Phase Columns per the current USP Method.
In this simple isocratic Method, we retain this polar compound with good Run-to-Run Precision. (%RSD = 0.22, SD below 0.004.) This Method can be easily transferred to LCMS.
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-75P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75mm
Mobile Phase: (50:50) DI Water with 0.1% Formic Acid / Acetonitrile
Injection vol.: 1µL
Flow rate: 1.0mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 220nm
Sample Preparation: Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride 2.0mg / mL in Mobile Phase.
Notes: Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It functions by inhibiting cell replication by preventing production of DNA gyrase, an enzyme which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. It is marketed worldwide under the brand name Avelox for oral treatment.

Attachment
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.1 Mb Download File
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride requires the addition of buffers as well as ion pair reagents to aid in retention on regular Reversed Phase Columns per the current USP Method.
In this simple isocratic Method, we retain this polar compound with good Run-to-Run Precision. (%RSD = 0.22, SD below 0.004.) This Method can be easily transferred to LCMS.
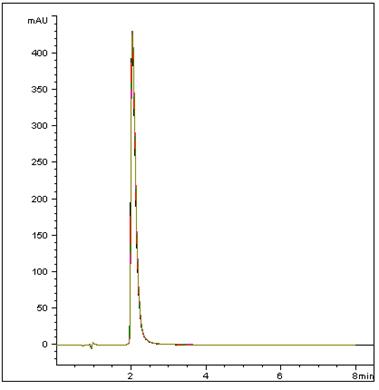
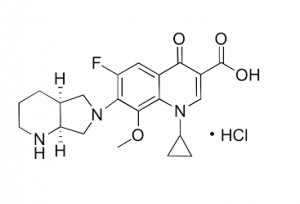
Peak:
Moxifloxacin hydrochloride
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-75P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75mm
Mobile Phase: (50:50) DI Water with 0.1% Formic Acid / Acetonitrile
Injection vol.: 1µL
Flow rate: 1.0mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 220nm
Sample Preparation: Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride 2.0mg / mL in Mobile Phase.
Notes: Moxifloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It functions by inhibiting cell replication by preventing production of DNA gyrase, an enzyme which allows the untwisting required to replicate one DNA double helix into two. Notably the drug has 100 times higher affinity for bacterial DNA gyrase than for mammalian. It is marketed worldwide under the brand name Avelox for oral treatment.

Attachment
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.1 Mb Download File
