Doxycycline Analyzed with HPLC - AppNote
May 21, 2012
/
/
/
/
/
Forced Degradation Method Using Shape Selectivity
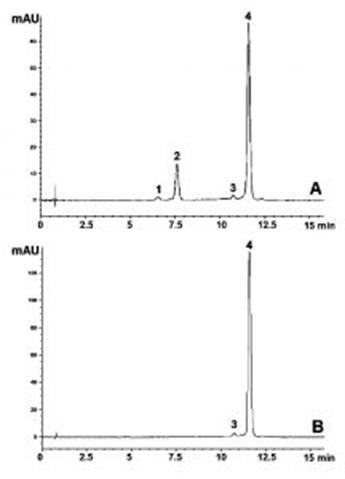
Doxycycline is known to epimerize at the C4 and C6 positions in acid conditions. Epimers can be difficult to separate in Reversed Phase due to subtle differences in hydrophobicity. However, this Method differentiates based on shape as well as hydrophobicity and is therefore well suited to this Isomer separation.
The method not only meets the USP System Suitability requirements for resolution between the API and both Epimer Degradants, but also demonstrates resolution from the Methacycline impurity.
Column: Cogent UDC-Cholesterol™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 69069-7.5P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA)
Gradient:
Temperature: 25˚C
Post Time: 3 minutes
Flow rate: 1.5mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 350nm
Injection vol.: 20μL
Sample Preparation:
--Figure A. Doxycycline forced Degradation extract
--Figure B. Doxycycline non-Degraded extract
100 mg strength doxycycline Hyclate tablets were ground and added to 50mL volumetric flasks. Portions of diluent were added and the flasks were sonicated for 10 minutes. After diluting to mark, portions were filtered with a 0.45µm Nylon Syringe Filter and each diluted 1:200. The diluents used were 50% 1N HCl / 50% Solvent B for Figure. A and 50% Solvent A / 50% Solvent B for Figure. B. The extract used in Figure A was also heated at 80°C for 30 minutes.
t0: 0.8 minutes
Note: Doxycycline is a member of the tetracycline class of antibiotics. It can be used to treat various kinds of bacterial infections.

Attachment
No 161 Doxycycline Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.2 Mb
Doxycycline is known to epimerize at the C4 and C6 positions in acid conditions. Epimers can be difficult to separate in Reversed Phase due to subtle differences in hydrophobicity. However, this Method differentiates based on shape as well as hydrophobicity and is therefore well suited to this Isomer separation.
The method not only meets the USP System Suitability requirements for resolution between the API and both Epimer Degradants, but also demonstrates resolution from the Methacycline impurity.


Peaks:
1. Epimer degradant
2. Epimer degradant
3. Methacycline
4. Doxycycline
Column: Cogent UDC-Cholesterol™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 69069-7.5P
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 0.1% Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA)
—B: Acetonitrile / 0.1% Trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 5 |
| 12 | 30 |
| 13 | 5 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Flow rate: 1.5mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 350nm
Injection vol.: 20μL
Sample Preparation:
--Figure A. Doxycycline forced Degradation extract
--Figure B. Doxycycline non-Degraded extract
100 mg strength doxycycline Hyclate tablets were ground and added to 50mL volumetric flasks. Portions of diluent were added and the flasks were sonicated for 10 minutes. After diluting to mark, portions were filtered with a 0.45µm Nylon Syringe Filter and each diluted 1:200. The diluents used were 50% 1N HCl / 50% Solvent B for Figure. A and 50% Solvent A / 50% Solvent B for Figure. B. The extract used in Figure A was also heated at 80°C for 30 minutes.
t0: 0.8 minutes
Note: Doxycycline is a member of the tetracycline class of antibiotics. It can be used to treat various kinds of bacterial infections.

Attachment
No 161 Doxycycline Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.2 Mb
