Separation of Inosine Nucleotides - AppNote
July 5, 2013
/
/
/
/
/
IMP, IDP, and ITP Analyzed by HPLC
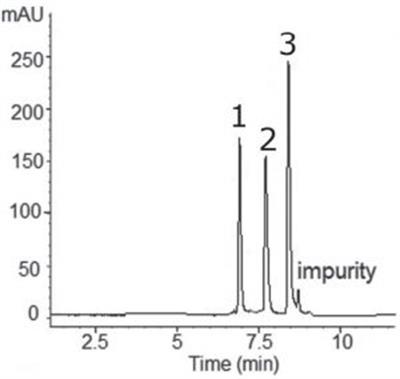
The figure shows the optimized separation of ITP (Inosine 5’-monophosphate), IDP (Inosine 5’-diphosphate) and IMP (Inosine 5’-triphosphate) in the order of increasing Phosphate content similar to anion exchange. The presence of at least one impurity near ITP and possibly a second near IMP precluded accurate determination of peak symmetry.
Column: Cogent UDA™, 4µm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 40031-05P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 50mm
Mobile Phase:
--A: DI Water / 16.0mM Ammonium Formate
--B: 90% Acetonitrile / 10% DI Water / 16.0mM Ammonium Acetate
Gradient:
Temperature: 25˚C
Post Time: 3 minutes
Injection vol.: 1 μL
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 254nm
Sample Preparation: Stock Solution: 1mg / mL solutions in DI Water. Samples were diluted 1:10 into 50% Acetonitrile / 50% DI Water mixture. Before injection, samples were filtered through a 0.45µm Nylon Syringe Filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp).
t0: 0.7 minutes
Note: Deficiency of the enzyme ITP Pyrophosphohydrolase is a common genetic defect in human populations and has aroused recent interest for its putative pharmacogenetic relevance to Thiopurine therapy. The enzyme is part of a nucleotide ‘‘futile cycle’’, which converts IMP to IDP and ITP then back to IMP.

Attachment
No 261 Separation of Inosine Nucleotides pdf 0.2 Mb Download File
The figure shows the optimized separation of ITP (Inosine 5’-monophosphate), IDP (Inosine 5’-diphosphate) and IMP (Inosine 5’-triphosphate) in the order of increasing Phosphate content similar to anion exchange. The presence of at least one impurity near ITP and possibly a second near IMP precluded accurate determination of peak symmetry.


Peaks:
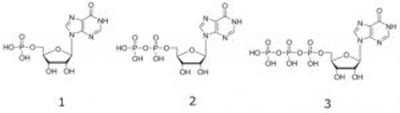
1. IMP – Inosine 5’-monophosphate
2. IDP – Inosine 5’-diphosphate
3. ITP – Inosine 5’-triphosphate
Column: Cogent UDA™, 4µm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 40031-05P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 50mm
Mobile Phase:
--A: DI Water / 16.0mM Ammonium Formate
--B: 90% Acetonitrile / 10% DI Water / 16.0mM Ammonium Acetate
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 100 |
| 1.5 | 100 |
| 13 | 30 |
| 20 | 30 |
| 20.1 | 100 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Injection vol.: 1 μL
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Detection: UV @ 254nm
Sample Preparation: Stock Solution: 1mg / mL solutions in DI Water. Samples were diluted 1:10 into 50% Acetonitrile / 50% DI Water mixture. Before injection, samples were filtered through a 0.45µm Nylon Syringe Filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp).
t0: 0.7 minutes
Note: Deficiency of the enzyme ITP Pyrophosphohydrolase is a common genetic defect in human populations and has aroused recent interest for its putative pharmacogenetic relevance to Thiopurine therapy. The enzyme is part of a nucleotide ‘‘futile cycle’’, which converts IMP to IDP and ITP then back to IMP.

Attachment
No 261 Separation of Inosine Nucleotides pdf 0.2 Mb Download File
