Histamine and methylhistamine analyzed with LCMS - AppNote
July 30, 2012
/
/
/
/
/
No derivatization required for detection or retention with this method
Various assay methods for histamine (HA) and / or its metabolite, methylhistamine (MHA), in biological samples, have been developed. However, most of them require post-column (for detection purposes) or pre-column (to achieve retention) derivatization.
The method in this application note provides separation and detection of these two compounds yet doesn’t require any derivatization. It is able to solve the inherently difficult problem of analyzing two biogenic amines with close physicochemical properties. A successful validation of the assay was indicated by the high linearity of calibration curves and the low inter- and intraday variation coefficients.
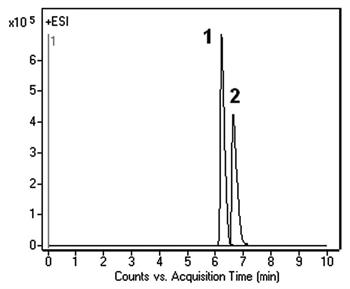
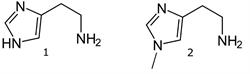
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-15P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 150mm
Mobile Phase:
--A: DI water with 0.1% formic acid (v/v)
--B: Acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid (v/v)
Gradient:
Post Time: 2 minutes
Injection vol.: 1µL
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Detection: ESI – POS - Agilent 6210 MSD TOF Mass Spectrometer
Sample Preparation: 1mg / mL of each compound was dissolved in DI water and filtered through a 0.45µm syringe filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp). Sample for injection was diluted 1:100 with 50:50 solvent A / solvent B mixture.
t0: 0.9 minutes

Attachment
No 197 Histamine and methylhistamine analyzed with LCMS Download File
Various assay methods for histamine (HA) and / or its metabolite, methylhistamine (MHA), in biological samples, have been developed. However, most of them require post-column (for detection purposes) or pre-column (to achieve retention) derivatization.
The method in this application note provides separation and detection of these two compounds yet doesn’t require any derivatization. It is able to solve the inherently difficult problem of analyzing two biogenic amines with close physicochemical properties. A successful validation of the assay was indicated by the high linearity of calibration curves and the low inter- and intraday variation coefficients.


Peaks:
1. Histamine 112.0869 m/z [M+H]+
2. Methylhistamine 126.1026 m/z [M+H]+
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4μm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-15P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 150mm
Mobile Phase:
--A: DI water with 0.1% formic acid (v/v)
--B: Acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 70 |
| 2 | 65 |
| 6 | 10 |
| 8 | 10 |
| 9 | 70 |
Injection vol.: 1µL
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Detection: ESI – POS - Agilent 6210 MSD TOF Mass Spectrometer
Sample Preparation: 1mg / mL of each compound was dissolved in DI water and filtered through a 0.45µm syringe filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp). Sample for injection was diluted 1:100 with 50:50 solvent A / solvent B mixture.
t0: 0.9 minutes

Attachment
No 197 Histamine and methylhistamine analyzed with LCMS Download File
