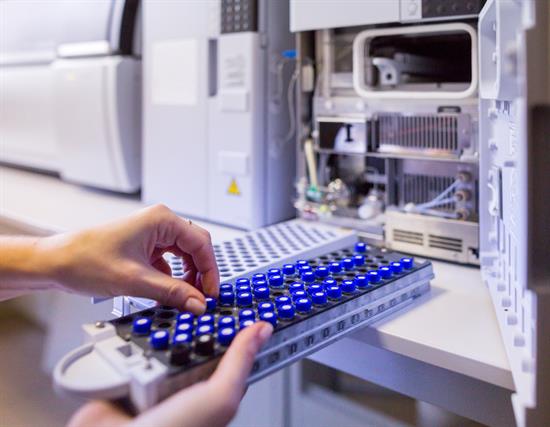
Thank you for considering MICROSOLV for your laboratory supplies and needs. We are dedicated to providing an unparalleled customer experience, placing your satisfaction at the top of our priorities.
We want your business and we want to earn it. Your Customer Experience is our top priority. MICROSOLV is unlike any other company in the Laboratory Supplies Industry. We were built with and live by tried and true ideals of Science and Customer Satisfaction helping all customers find solutions to their Filtration and Separation challenges or needs. We offer State-of-the-Art technologies along with products you are familiar with at exceptional value making us a choice of scientists worldwide.
As a resource for you, our Technical Support is effective, easy to use and available 24 hours a day through our online Resource Center or you can contact our highly experienced Support Team directly between the hours of 9:00AM and 6:00PM Eastern Time.
Thank you for visiting our website, we are happy you are here! Now, discover the “MICROSOLV experience” it will make a difference and you will not be disappointed.