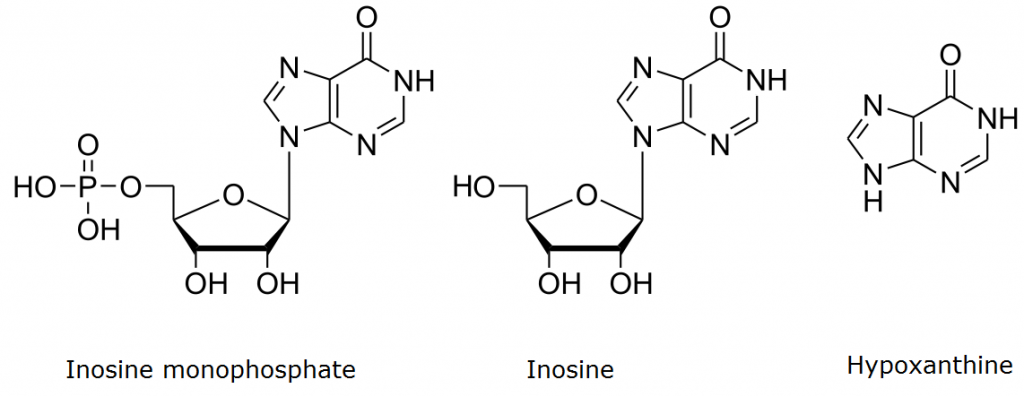
All nucleotides are are comprised of the following sub-structures: A nucleobase, a 5-membered ring sugar unit (either ribose or 2-deoxyribose), and one or more phosphate groups.
In the case of inosine nucleotides, the nucleobase is hypoxanthine. When a ribose unit is attached to hypoxanthine via a β-N9-glycosidic bond, it is known as the nucleoside inosine. It is the presence of phosphate groups that distinguishes a nucleotide from a nucleoside.