Analysis of Polar Antibiotic Main Active Ingredient: Cephalexin Monohydrate
Cephalexin Monohydrate, commercially known as Keflex, is a semi synthetic Cephalosporin antibacterial drug, analysis of which is of great interest to scientists from many research fields. There is a need for a rapid, efficient and inexpensive analytical method to be applied for analysis of formulations during industrial process development as well as for monitoring of the drug level in patients after administration.
In the Chromatogram shown below, Keflex was sufficiently retained using a gradient HPLC method and the Cogent Diamond Hydride Column and the peak shape is very symmetrical. The advantages of using the selected column and method are: fast equilibration between runs when gradient analysis is used, and very easy transfer to MS detection. Due to the high organic content of the Mobile Phase used, the ionization efficiency of an MS detector would be much better when compared to the Mobile Phase with a high concentration of Water.
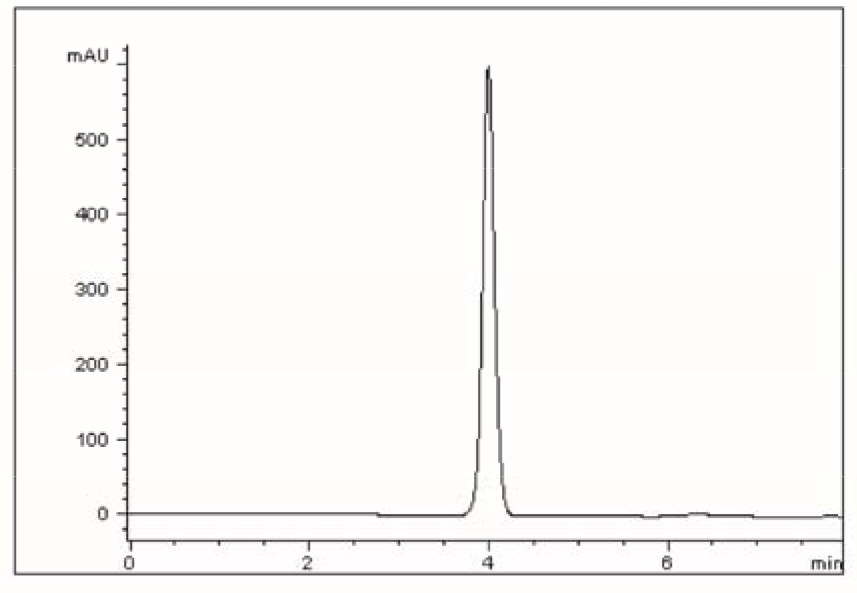
PEAK:
Cephalexin Monohydrate
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4µm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000 -7.5
Dimensions: 4.6 x 75mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water with 0 .1% Formic Acid
—B: 90:5 Acetonitrile / 0.1% Formic Acid
Gradient:
| Time (Minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 90 |
| 1 | 90 |
| 4 | 20 |
| 5 | 20 |
| 6 | 90 |
Injection vol.: 5µl
Flow rate: 1.0ml / minute
Detection: UV @ 260nm
Sample Preparation: Cefalexin ; Keflex. Final concentration: 1mg / ml in DI Water. The solution was filtered through a 0 .45µm Nylon Syringe Filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp).
Attachment
Antibiotic Keflex Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.3 Mb Download File


