Analysis in Urine Samples
An enzymatic Method is widely used for the determinations of Glycolic Acid in various products, but it suffers from instability and very high cost of the enzyme (Glycolate Oxidase). The LCMS analysis presented here is rapid, simple, selective, and suitable for routine analyses of urine samples.
It offers numerous advantages including ease of sample preparation, low cost, rapidity, and excellent repeatability (precision was better than 1.0% – %RSD below 0.5 for n=3). The calibration curve was linear in the 0.080–0.30 mg / mL (GA). The correlation coefficients of linear regression analysis were with the range 0.9974–0.9997. Recoveries of the GA from urine samples were between 94.9 and 100.5%.
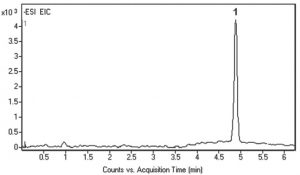
 Peak:
Peak:
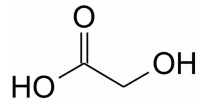
Glycolic Acid 75.0088 [M-H]– m/z in urine sample
Method Conditions
Column: Cogent Diamond Hydride™, 4µm, 100Å
Catalog No.: 70000-15P-2
Dimensions: 2.1 x 150mm
Mobile Phase:
—A: DI Water / 10 mM Ammonium Formate
—B: 95% Acetonitrile / 5% DI Water / 10 mM Ammonium Formate (v/v)
Gradient:
| Time (minutes) | %B |
| 0 | 95 |
| 1 | 95 |
| 5 | 30 |
| 7 | 30 |
| 8 | 95 |
Post Time: 3 minutes
Flow rate: 0.4mL / minute
Detection: ESI – NEG – Agilent 6210 MSD TOF Mass Spectrometer
Sample Preparation: Urine sample was spiked with stock solution of Glycolic Acid. The solution was filtered through a disposable 0.45µm Syringe Filter (MicroSolv Tech Corp.). The sample for injection was diluted 1:100 with 50:50 Solvent A / Solvent B mixture for a final concentration of 0.1mg / mL.
t0: 0.9 minutes
Note: Glycolic Acid is widely used in adhesives, metal cleaning, dairy cleaning, water-well cleaning, electroplating, dyeing, detergents and cosmetic products. It is also the most commonly used hydrophilic teeth whitening agent.
Attachment
No 220 Glycolic Acid Analyzed with HPLC pdf 0.2 Mb Download File


